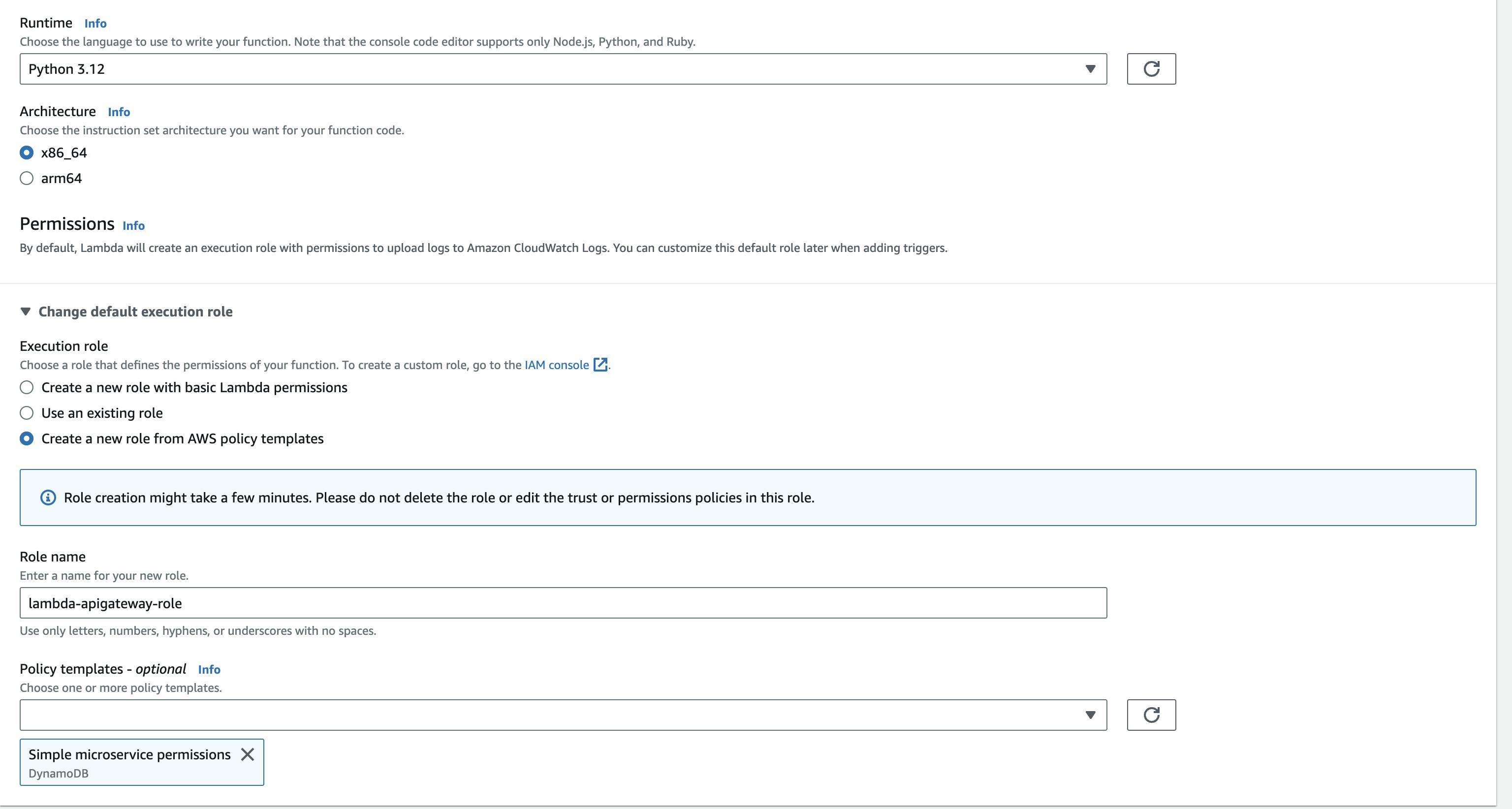
Step-1: Create a policy and execution role for lambda to access DynamoDB.
You can do this while creating the lambda function. You will be required to select a simple microservice permission policy template.
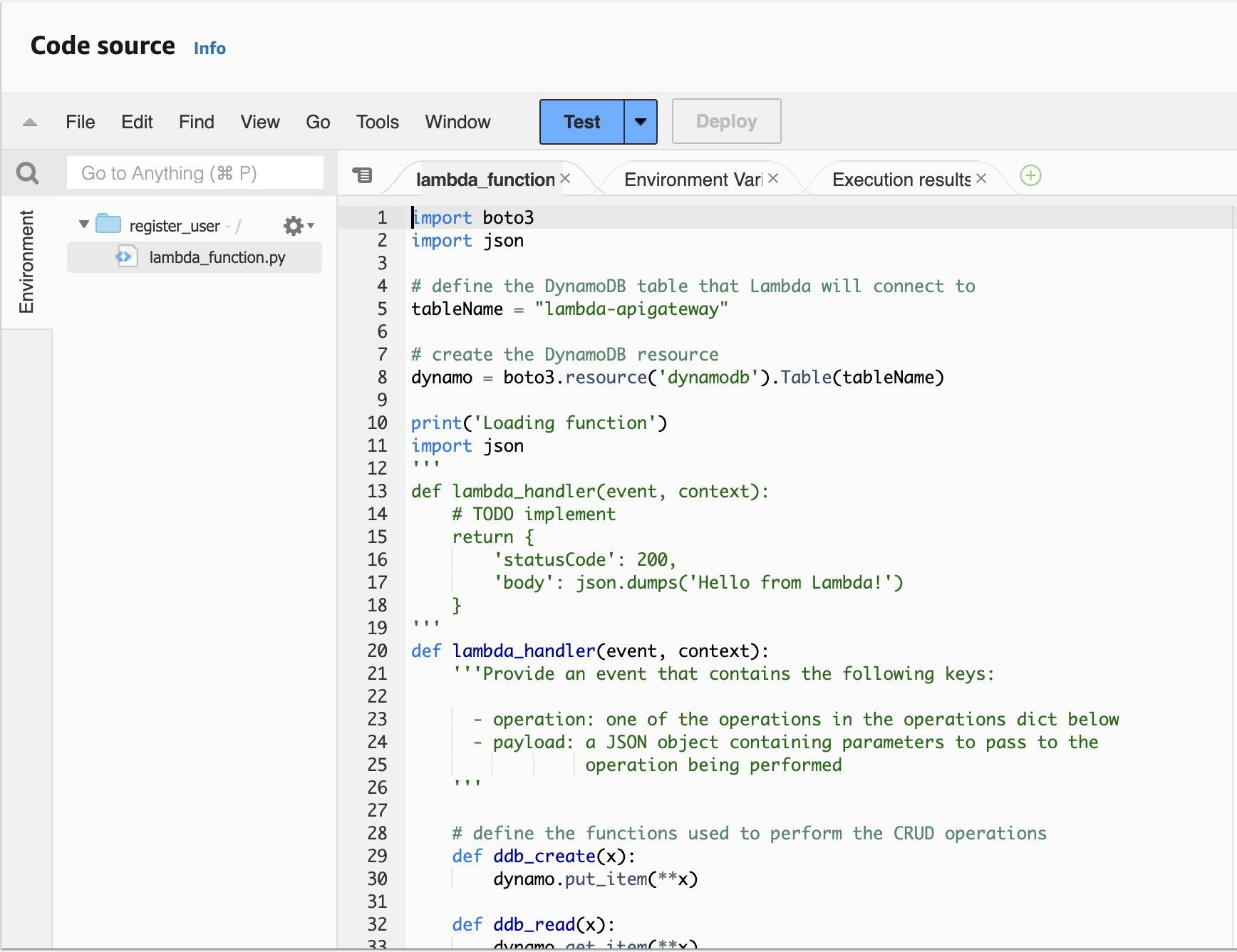
Step 2: Create a lambda function with the below code.
You can do this by copying this code to the lambda_function.py and then deploy the code.
import boto3
import json
# define the DynamoDB table that Lambda will connect to
tableName = "lambda-apigateway"
# create the DynamoDB resource
dynamo = boto3.resource('dynamodb').Table(tableName)
print('Loading function')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
'''Provide an event that contains the following keys:
- operation: one of the operations in the operations dict below
- payload: a JSON object containing parameters to pass to the
operation being performed
'''
# define the functions used to perform the CRUD operations
def ddb_update(x):
dynamo.update_item(**x)
def echo(x):
return x
operation = event['operation']
operations = {
'update': ddb_update,
'echo': echo,
}
if operation in operations:
return operations[operation](event.get('payload'))
else:
raise ValueError('Unrecognized operation "{}"'.format(operation))
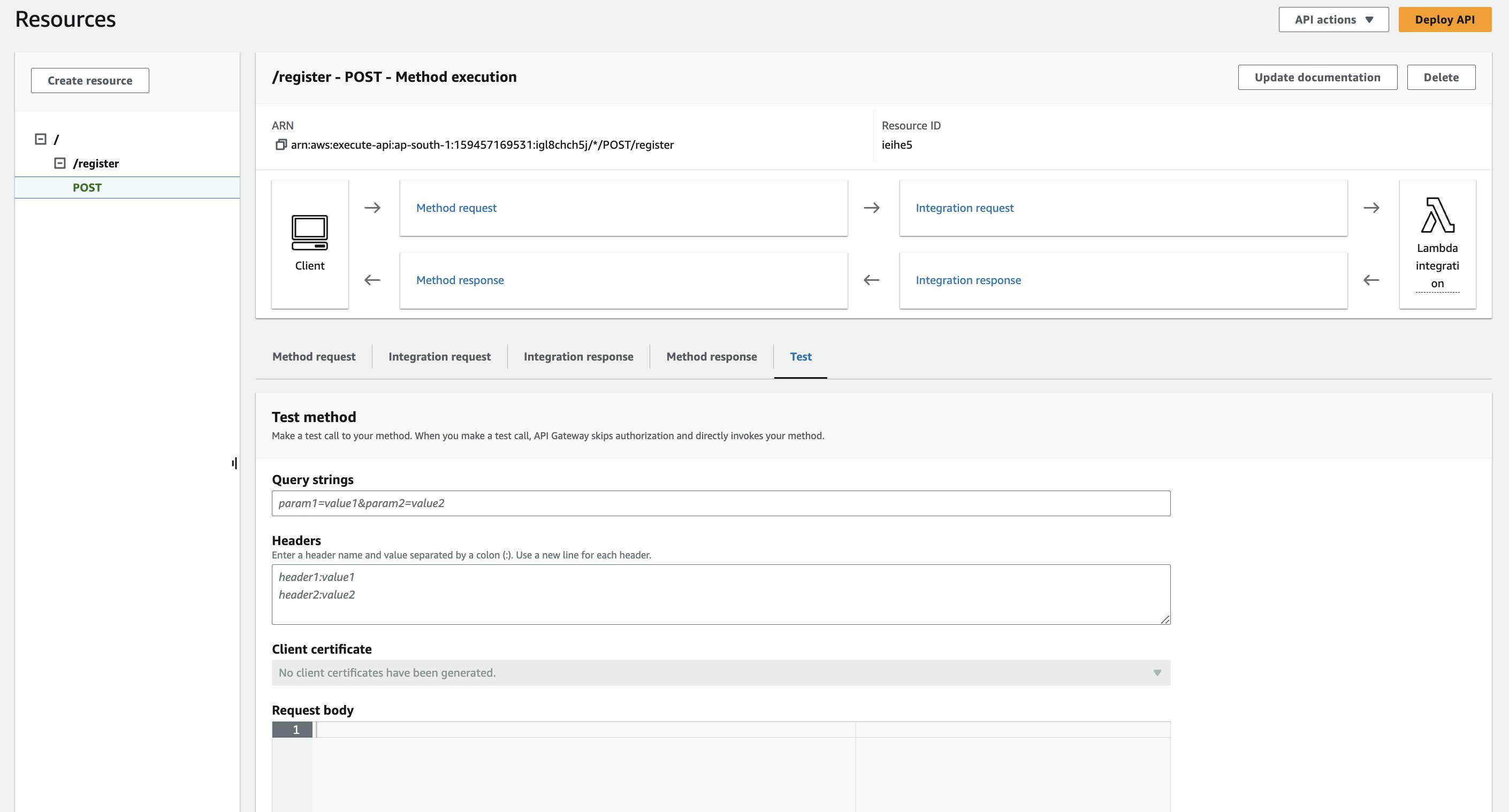
Step-3: Create a REST API through api gateway.
First, you need to create a resource register. After creating a resource you need to create a post method. After creating a post create a new stage and deploy.
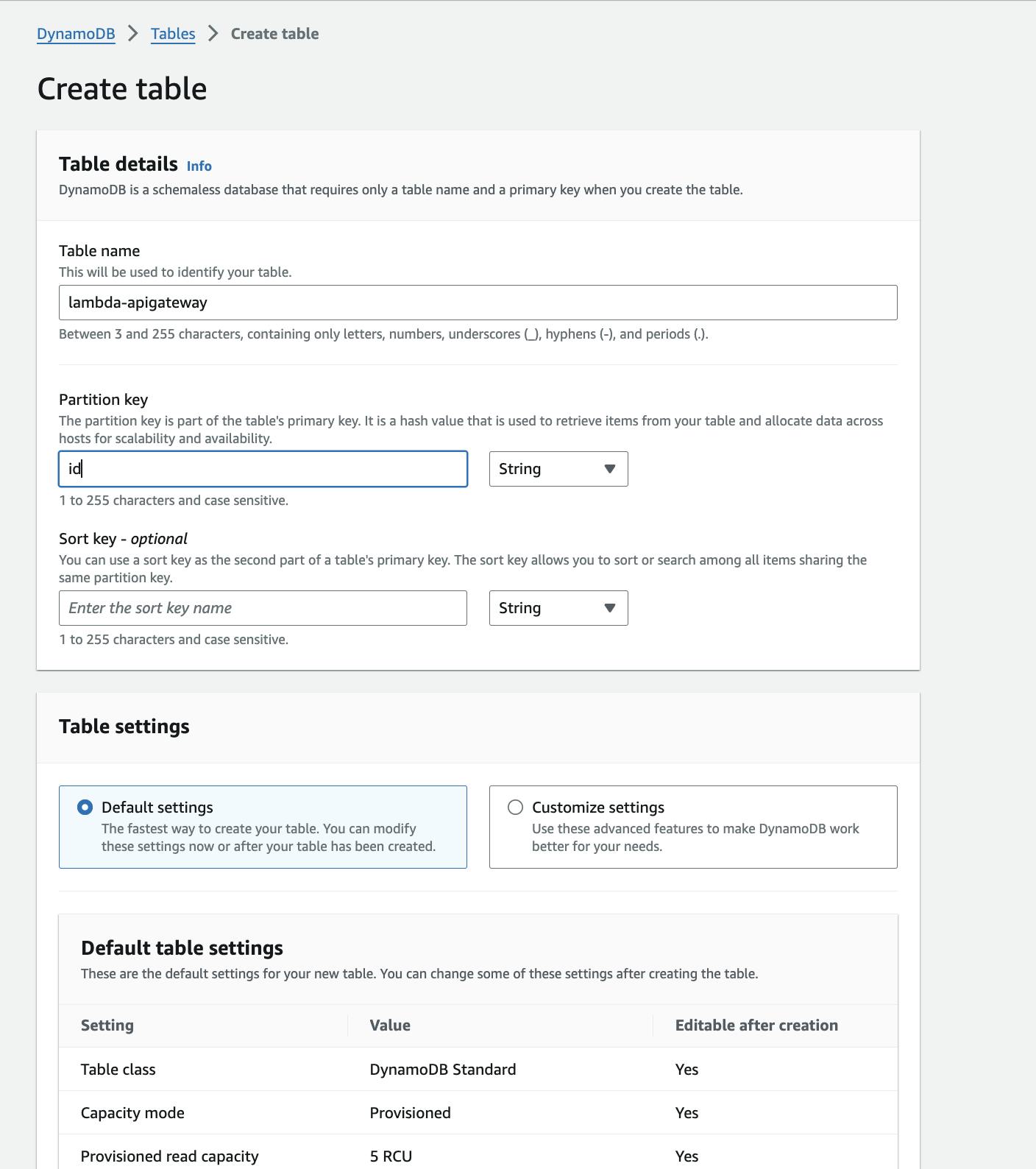
Step-4: Create a dynamodb to store user data.
Please create a dynamodb with lambda-API gateway as the table name and id as the partition key as shown below.
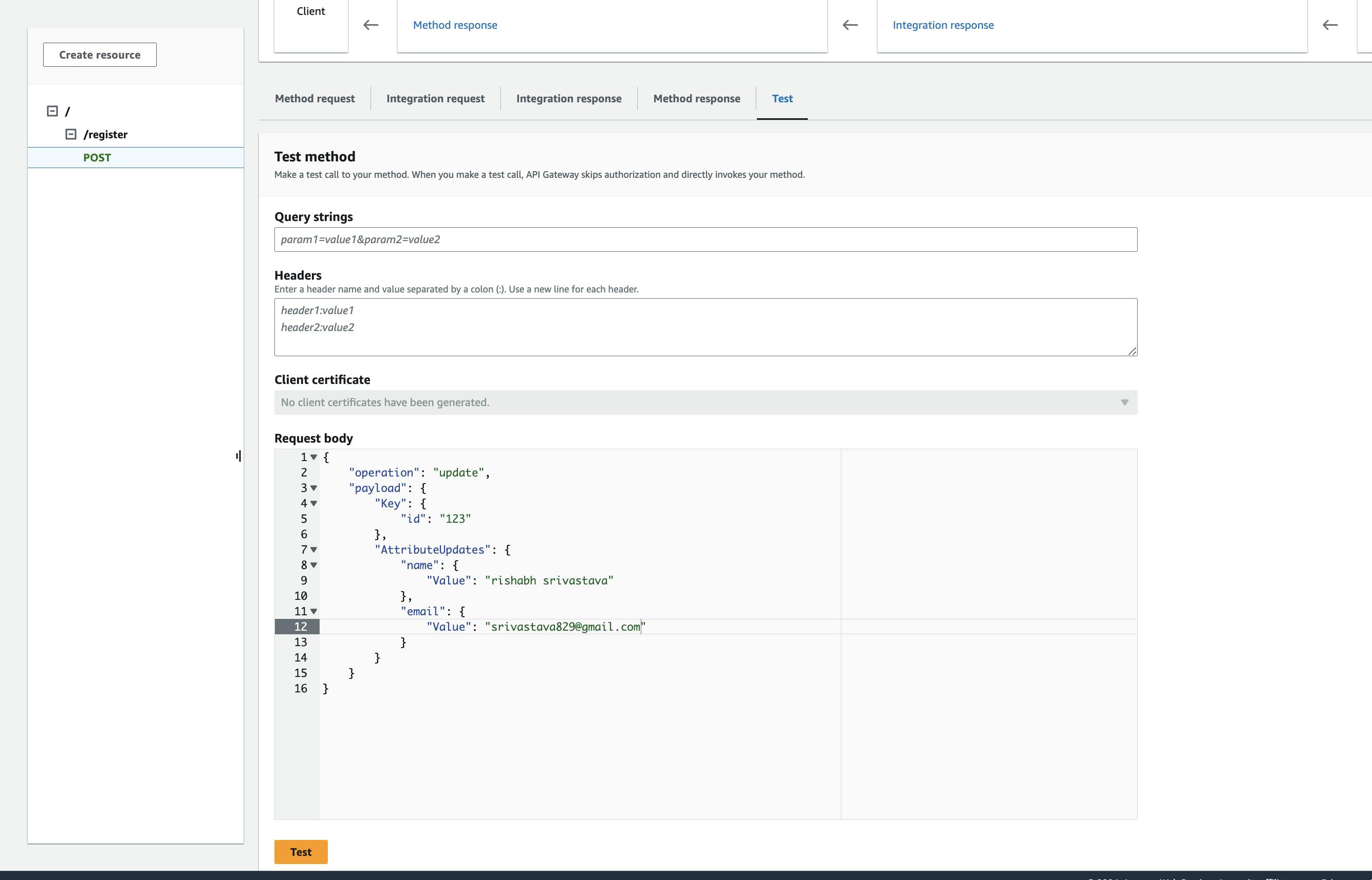
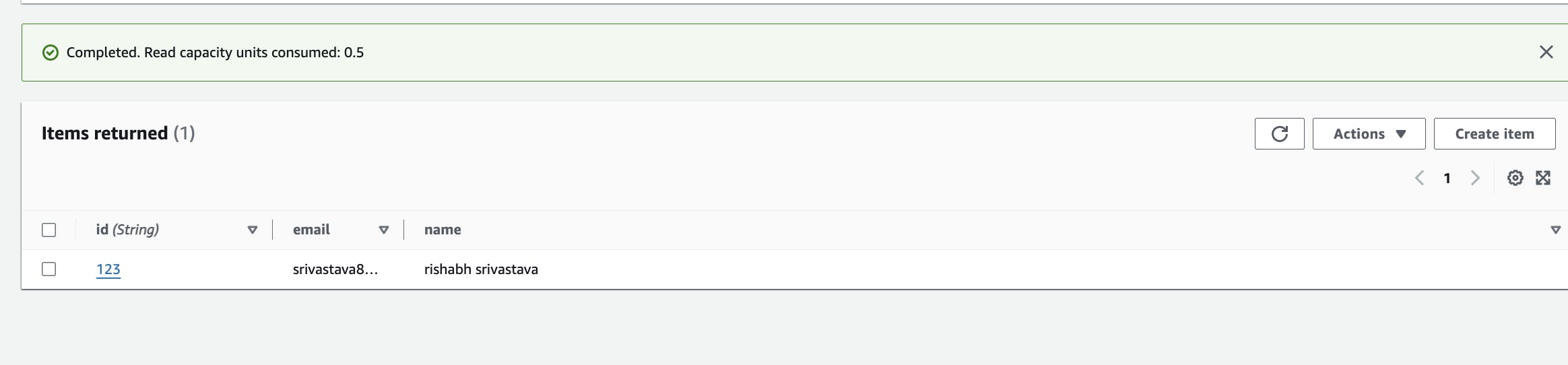
Step-5: After dynamo db is created use the below input to create an entry in dynamodb to test the function. by using the test function of api gateway.
{
"operation": "update",
"payload": {
"Key": {
"id": "1234ABCD"
},
"AttributeUpdates": {
"number": {
"Value": 10
}
}
}
}